Mapping the Ligand-binding Sites and Disease-associated Mutations on the Most Abundant Protein in the Human, Type I Collagen* - Journal of Biological Chemistry

Collagen Stimulating Effect of Peptide Amphiphile C16–KTTKS on Human Fibroblasts | Molecular Pharmaceutics
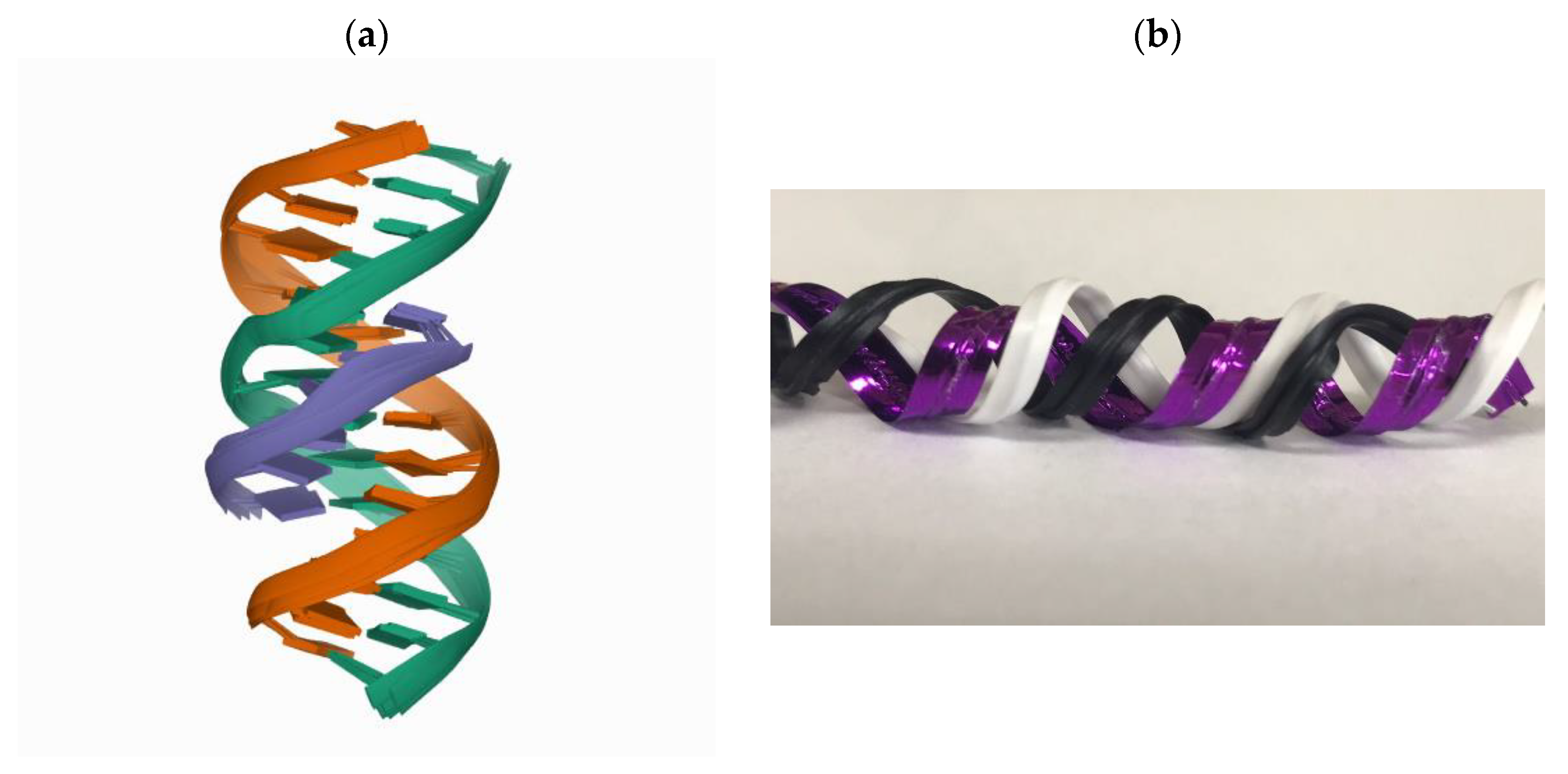

Polymers | Free Full-Text | A Review of the Effects of Collagen Treatment in Clinical Studies | HTML

Collagen Stimulating Effect of Peptide Amphiphile C16–KTTKS on Human Fibroblasts | Molecular Pharmaceutics
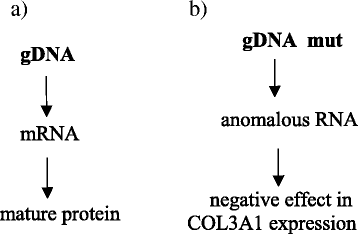
Genotype–phenotype correlations in nonlethal osteogenesis imperfecta caused by mutations in the helical domain of collagen type I | European Journal of Human Genetics
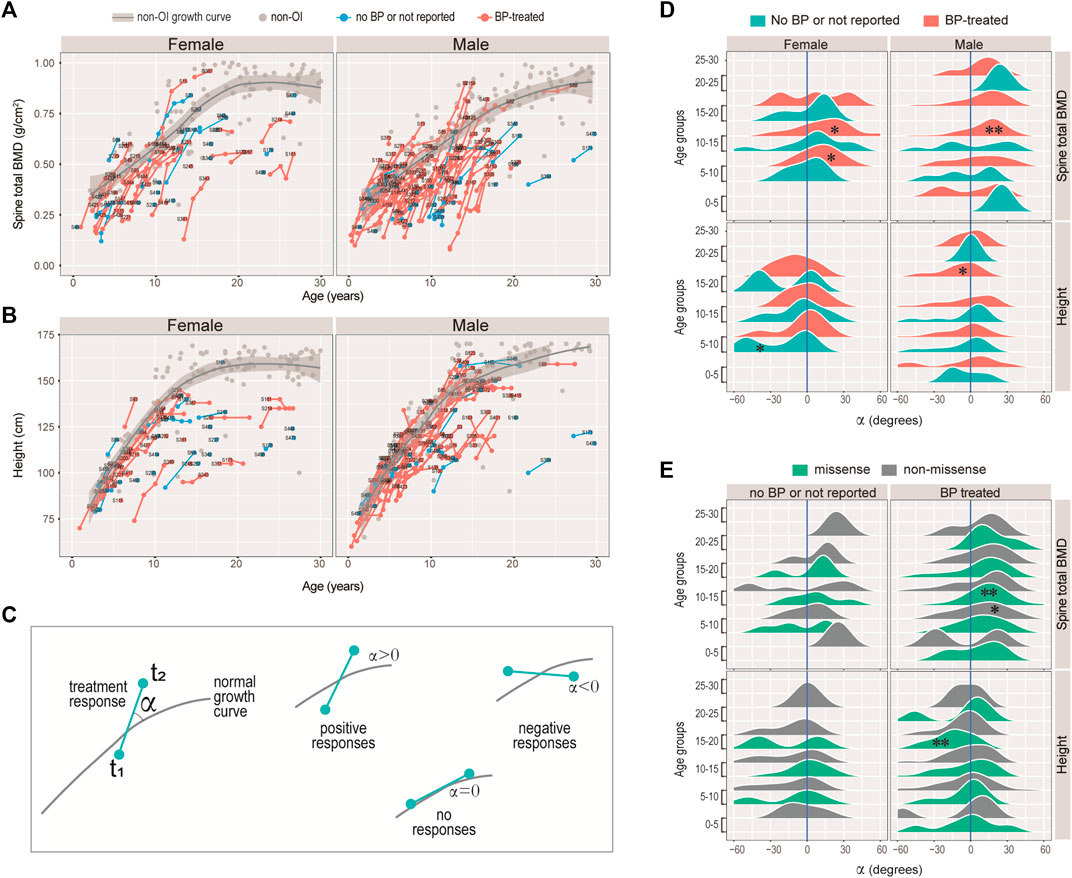
Frontiers | Phenotypic Spectrum and Molecular Basis in a Chinese Cohort of Osteogenesis Imperfecta With Mutations in Type I Collagen

Densified Collagen Tubular Grafts for Human Tissue Replacement and Disease Modelling Applications | bioRxiv
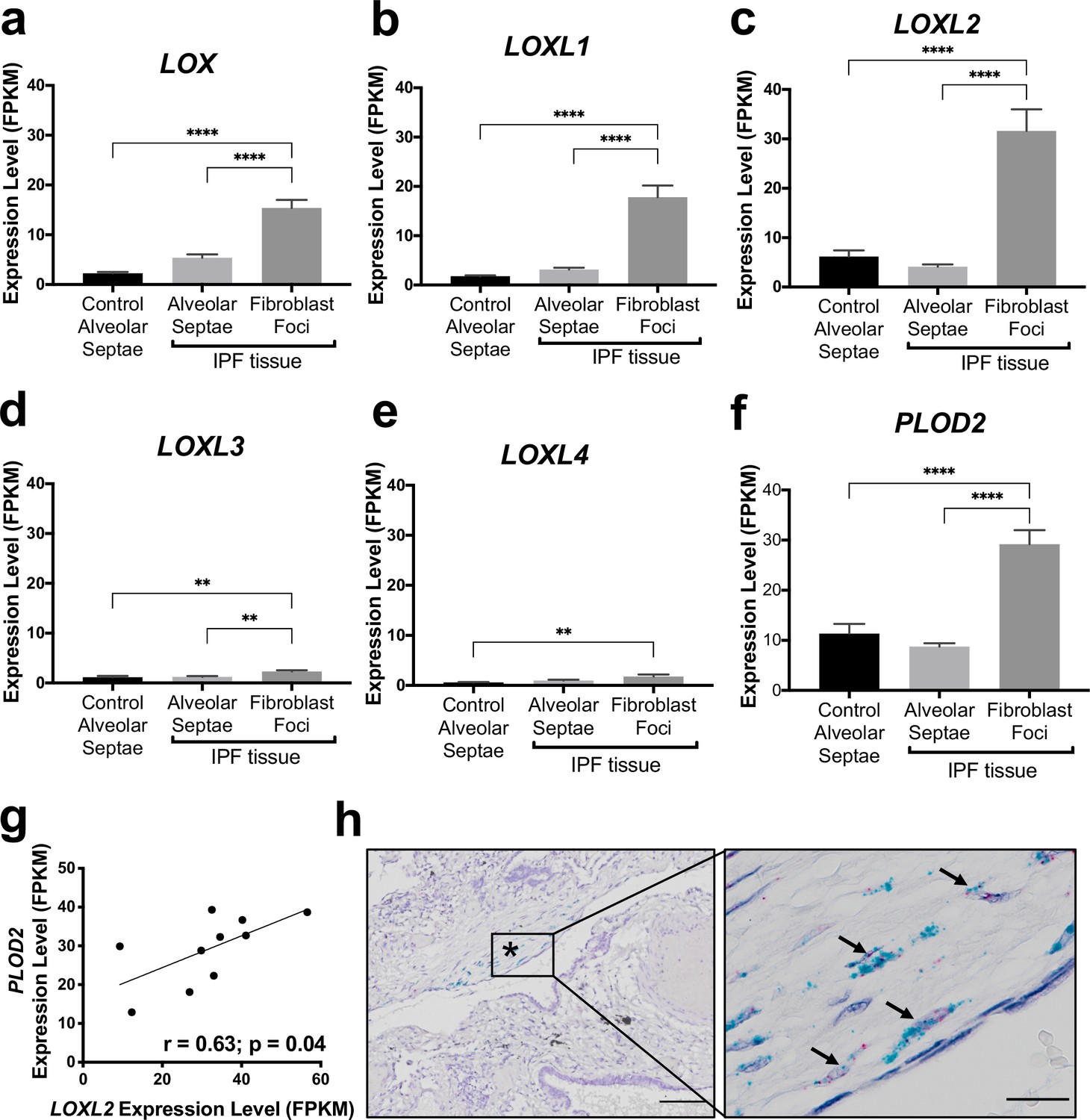
Pseudohypoxic HIF pathway activation dysregulates collagen structure-function in human lung fibrosis | eLife
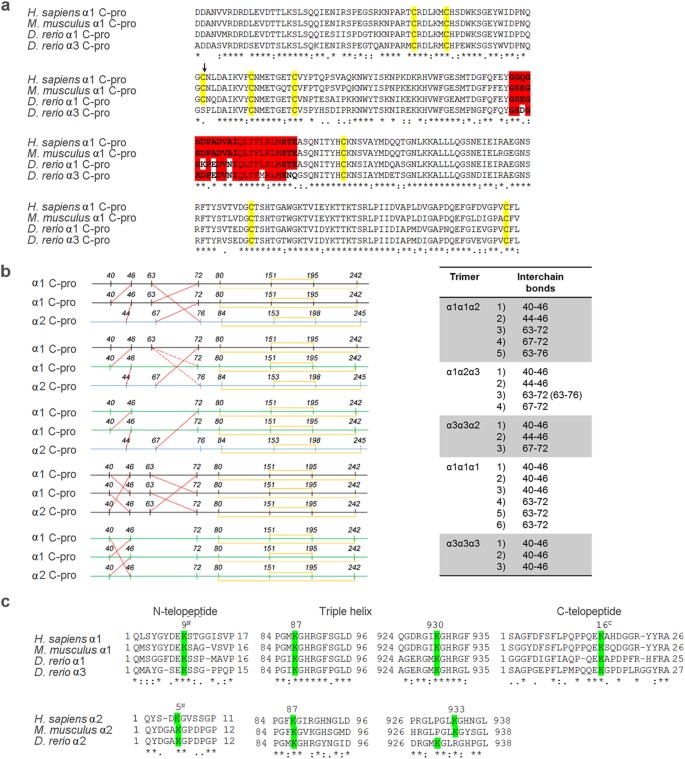
Zebrafish Collagen Type I: Molecular and Biochemical Characterization of the Major Structural Protein in Bone and Skin | Scientific Reports

Interaction of Axonal Chondrolectin with Collagen XIXa1 Is Necessary for Precise Neuromuscular Junction Formation - ScienceDirect

The triple helix of collagens - an ancient protein structure that enabled animal multicellularity and tissue evolution. - Abstract - Europe PMC
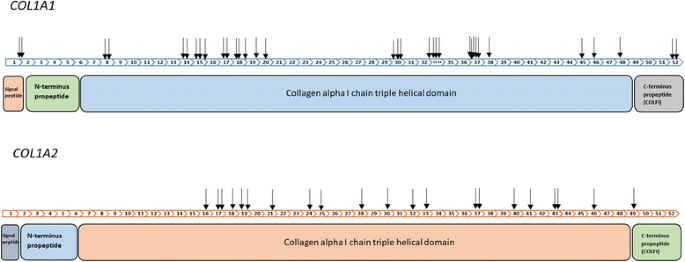
Mutation analysis of the COL1A1 and COL1A2 genes in Vietnamese patients with osteogenesis imperfecta | Human Genomics | Full Text
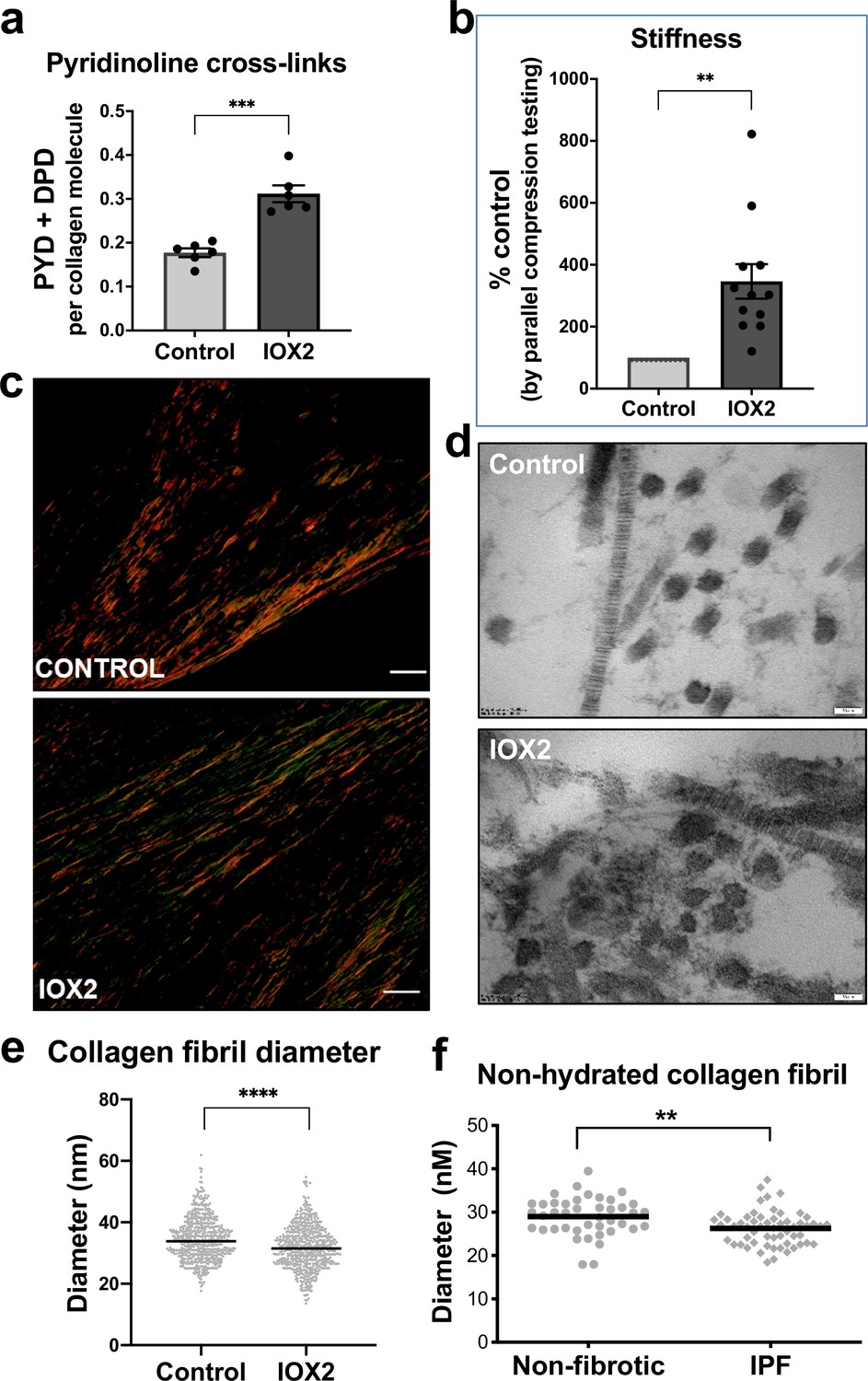
Pseudohypoxic HIF pathway activation dysregulates collagen structure-function in human lung fibrosis | eLife

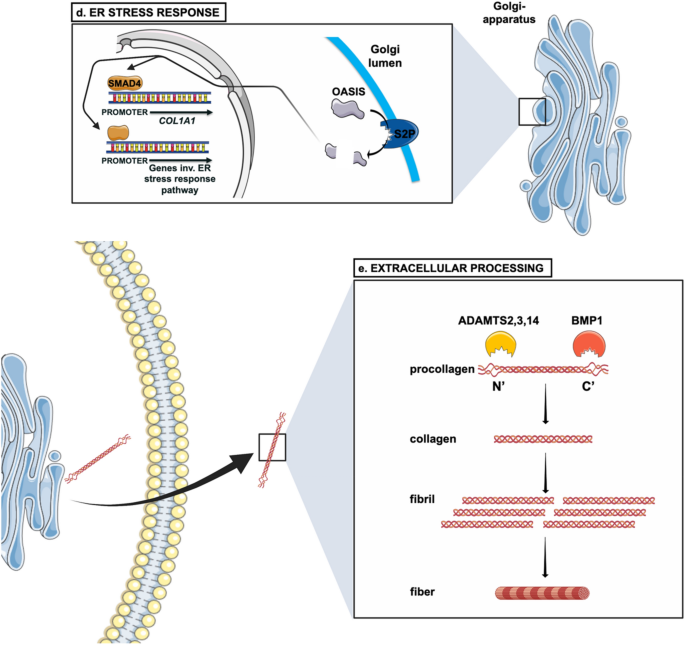
Bone Morphogenetic Protein-1 Processes the NH2-terminal Propeptide, and a Furin-like Proprotein Convertase Processes the COOH-terminal Propeptide of pro-α1(V) Collagen* - Journal of Biological Chemistry

Genotype–phenotype correlations in nonlethal osteogenesis imperfecta caused by mutations in the helical domain of collagen type I | European Journal of Human Genetics
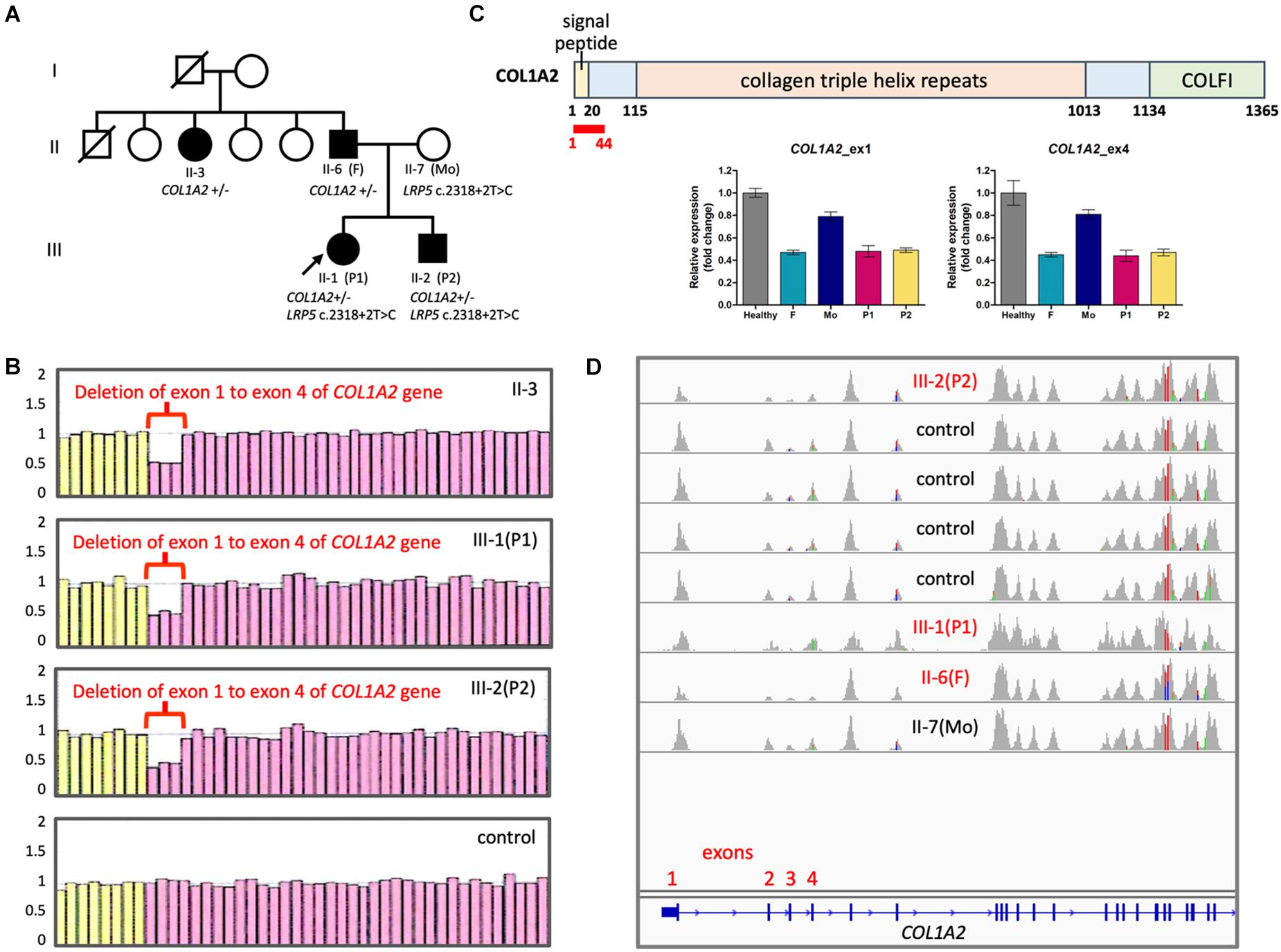
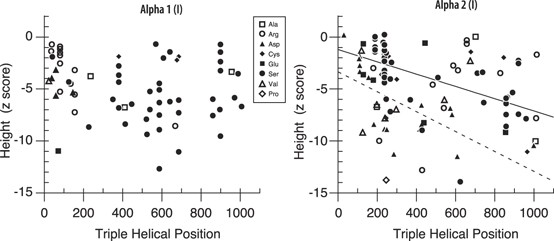
Frontiers | New Structural and Single Nucleotide Mutations in Type I and Type II Collagens in Taiwanese Children With Type I and Type II Collagenopathies

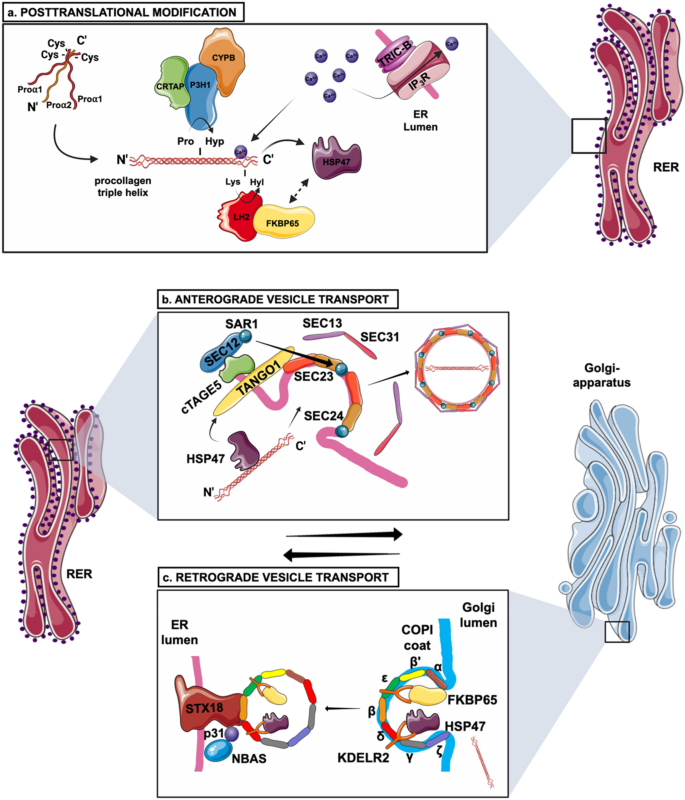
Candidate Cell and Matrix Interaction Domains on the Collagen Fibril, the Predominant Protein of Vertebrates - ScienceDirect

Collagen XVII Is Destabilized by a Glycine Substitution Mutation in the Cell Adhesion Domain Col15* - Journal of Biological Chemistry

Zebrafish Collagen Type I: Molecular and Biochemical Characterization of the Major Structural Protein in Bone and Skin | Scientific Reports
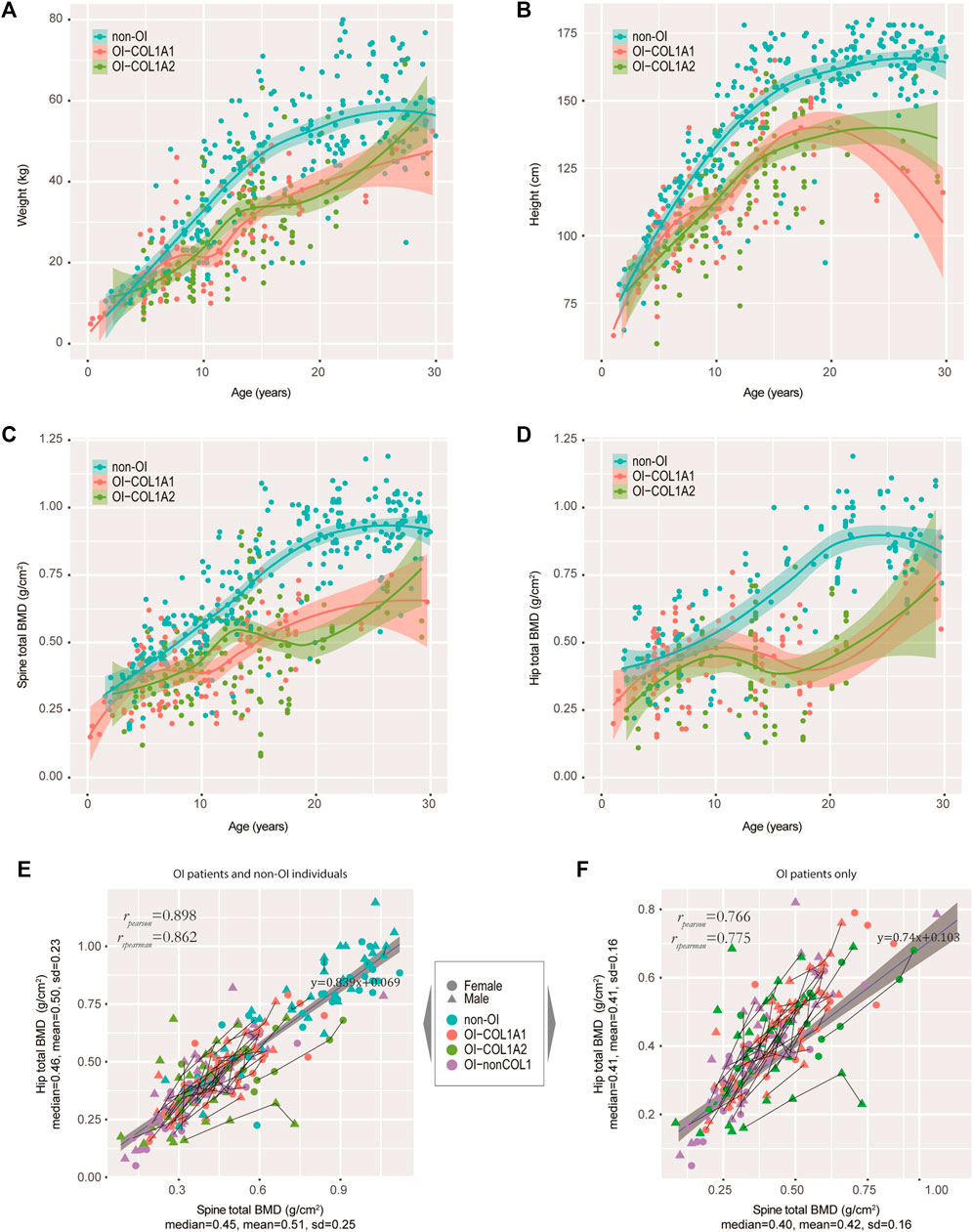
Frontiers | Phenotypic Spectrum and Molecular Basis in a Chinese Cohort of Osteogenesis Imperfecta With Mutations in Type I Collagen

Regulation of mineralisation in bone and vascular tissue: a comparative review in: Journal of Endocrinology Volume 248 Issue 2 (2021)